Secondary Growth In Plants Definition. Produced in one part of plant and act in another translocatable c. It increases the diameter of the stem. American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language Fifth Edition. While the principles are similar for secondary growth in roots the details are somewhat different.
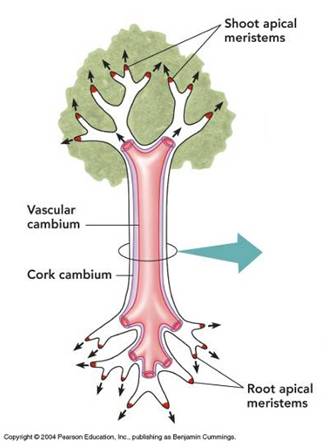
Secondary growth in plants refers to the development that occurs when cells divide into the lateral meristems or cambia. Secondary growth definition an increase in the thickness of the shoots and roots of a vascular plant as a result of the formation of new cells in the cambium. The details below are specific to secondary growth in stems. While the principles are similar for secondary growth in roots the details are somewhat different. Secondary growth causes both the roots and stems to thicken. Figure 4 shows the areas of primary and secondary growth in a plant.
The mature dicot stem shows secondary growth and increases in girth.
Secondary growth occurs in gymnosperms most eudicots and woody magnoliids such as the magnolia. Figure 4 shows the areas of primary and secondary growth in a plant. Secondary growth is the formation of secondary tissues from lateral meristems. The new tissue accumulates and results in thicker branches and stems. Secondary growth causes the plant to grow in width due to the presence of lateral meristems or cambium layer which. The primary growth occurs by the action of the apical meristem.