
Screening Effect In Chemistry. What is screening effect in chemistry. In a multielectron atom the valence shells electrons are attracted to the nucleus and these electrons are repelled by the electrons present in the inner shells. He stressed there is no single screening parameter which will represent all the properties. Normally the screening effect takes place for the elements which have a high atomic number and have a large number of electrons in their inner orbits.
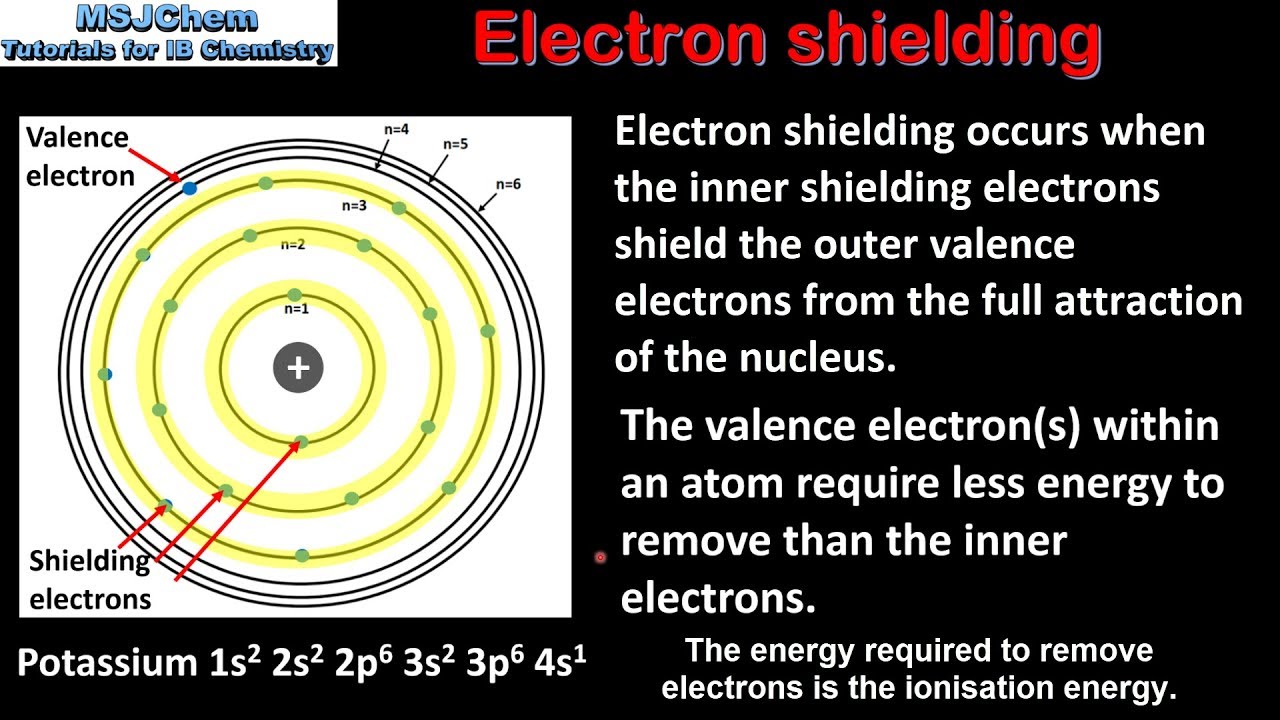
This result can be understood in terms of the screening of van der Waals and dipole interactions by the electrons in graphene. What is Screening Effect. The screening constant σ corrects the nuclear charge Z to Zσ. The screening effect depends only on the number of electron orbits inside the valence shell. On account of this the actual force of attraction between the nucleus and the valence electrons is somewhat decreased by the repulsive forces. For example the atoms across Period 3 have 3 shells occupied by electrons.
As the atomic number increases the screening constant increases and screening effect decreases.
The presence of high-quality monolayer graphene free of any air contaminants polymer residues etc led to a common wettability behaviour for all coated surfaces regardless of the nature of the underlying substrate. So the screening effect remains unchanged. Screening effect or shielding effect. Shielding effect can be defined as a reduction in the nuclear charge on the electron cloud due to a difference in the attraction forces of the electrons on the nucleus. What is Screening Effect. The screening effect is 1125.