
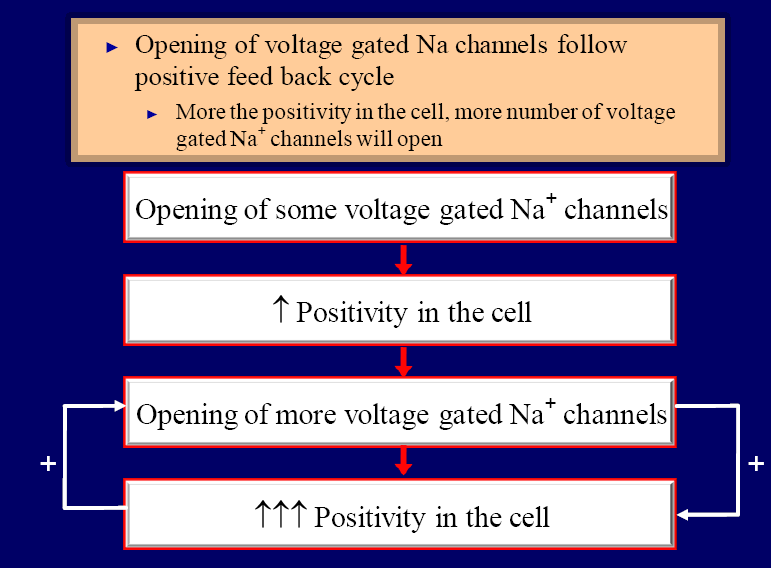
Safety Factor Action Potential. IQ2jNT6AXpE1Bul6 Videos you. The all-or-none law is a principle that states that the strength of a response of a nerve cell or muscle fiber is not dependent upon the. When the action potential reaches an area where all the cell membrane is already depolarized or still in the refractory period the action potential can no longer propagate. Review procedure and responsibility to initiate and carry out.
To determine if a reduced safety factor for conduction at the branch sites has a morphological basis the geometrical ratio GR. The rate of voltage decrease with distance will in turn depend on the relative resistance to current flow of the plasma membrane and the intracellular path down. If playback doesnt begin shortly try restarting your device. In the crayfish regions of axonal bifurcation where action potential propagation failed during repetitive activity were visualized using modulation-contrast optics. Safety factor for action 14. Ordinary muscle cells lack this property and can thus engage in what are called.
Ordinary muscle cells lack this property and can thus engage in what are called.
Safety factor is the ratio of action potential to threshold for excitation must at all times be greater than 1. This is essentially a safety factor. Safety factor for action 14. Conduction safety factor in axonal and dendritic compartments in dilute TTX To address potential concerns that the low Na manipulation could also affect other Na -dependent processes such as pumps and exchangers Bouron and Reuter 1996 we used a low dose of TTX 20 nM to attenuate the Na spike to a similar degree as 60 mM external Na range 4557 amplitude. FOS F fail F allow 1 where. This is a result of the amount of transmitter released per nerve impulse being greater than that required to trigger an action potential in the muscle fibre.