Physiological Effects Of Water Deficit In Plants. Effects of water deficits on physiological morphological and biological processes 1. Introduction what do you mean by physiological changes. To avoid this some Mediterranean annuals exhibit a phenological drought avoidance meaning that they flower and produce seed before water supplies are exhausted. This inactivates PSII reaction centers.

WATER RELATIONS OF PLANTS Drought Stress. One-year-old grapevine Vitis vinifera L. The purpose of the present study was the investigation of the effects of water deficit on physiological responses in grapevine. The book explains the effects under soil water deficit condition such as lowering of plant water content disturbance in carbon metabolism such in photosynthesis photorespiration and respiration as well as effects of soil water deficit on nitrogen metabolism. However as water potential of the dryland plants became more depressed during the afternoon the CER and light adapted PSII quantum efficiency of the dryland plants became inhibited and was 6 and 10 lower respectively than irrigated leaves. It is one of the major causes of crop loss worldwide.
Water deficits inhibit several aspects of cambial growth including.
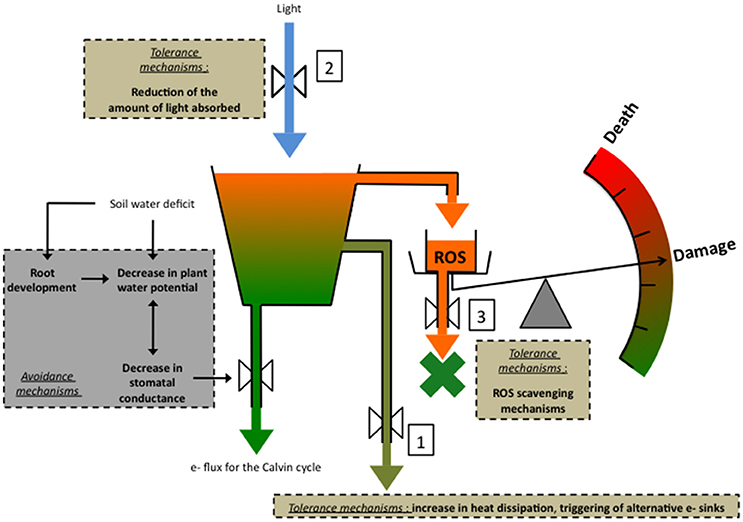
Additionally soil mulching led to a decrease in weed density and biomass chlorophyll content and biological yield. Water stress invariably increases excess energy absorbed causing photoinhibition. Water and nitrogen N are essential resources influencing plant growth and yieldTo improve their efficiencies in crop production is challenging because the physiological mechanisms of water and N coupling and their interactive effect on crop water use efficiency WUE are not well understood yet. A rapid osmotic phase that inhibits. Water deficit at cellular level i. It is one of the major causes of crop loss worldwide.