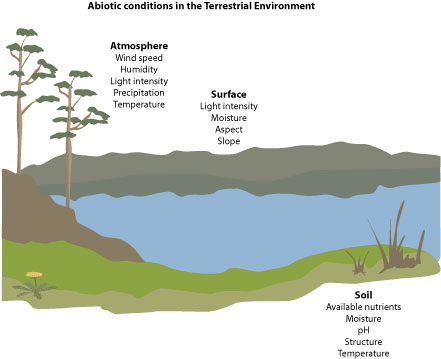
Measuring Abiotic Factors In An Ecosystem. Marine sea estuaries salt marches and mangroves. Measuring the pH and moisture of the soil Soil moisture and soil pH meters are used by simply pushing the probe into the soil and reading the meter. Freshwater Rivers lakes and wetlands 3. Abiotic factors refer to all the non-living ie.

Direct chemical tests are used to measure chemical pollutant levels to give us an indication about the concentration of pollutants. Errors can be made when measuring abiotic. Theres a wide variety of abiotic factors that influence what may live in an ecosystem some examples of which are listed below. Techniques for measuring abiotic factors. Measuring the pH and moisture of the soil Soil moisture and soil pH meters are used by simply pushing the probe into the soil and reading the meter. Temperature turbidity pH dissolved oxygen nitrate levels and phosphate levels.
Direct chemical tests are used to measure chemical pollutant levels to give us an indication about the concentration of pollutants.
Sunlight - The amount and intensity of regular sunlight exposure. Techniques for measuring abiotic factors. Abiotic factors are the nonliving elements like air water soil and temperature. Hydrometer measures specific gravity or density of a sample relative weight of 10L salt water compared to 10L pure fresh water refractometer measures. Sunlight air precipitation minerals and soil are some examples of abiotic factors. Salinity - many marine organisms tolerate a variety of salt concentration levels in the water which can be checked with a few tools.