
Income Equality In China. Analyzing comparable survey data collected in 2010 in China and the United States we examine social determinants that help explain Chinas high income inequality. In 2015 the bottom 50 per cent in China earn approximately 15 per cent of total national income versus 12 per cent in the USA and 22 per cent in France. China has experienced rapid economic growth over the past two decades and is on the brink of eradicating poverty. While the top 1 per cent earns about 14 per cent of national income versus 20 per cent in the USA and 10 per cent in France.
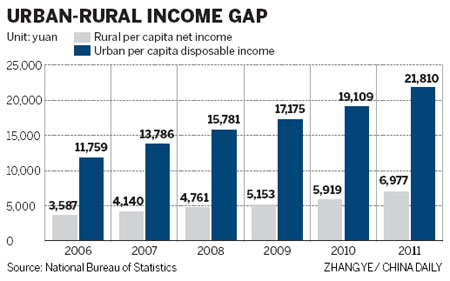
Using multiple data sources we establish that Chinas income inequality since 2005 has reached very high levels with the Gini coefficient in the range of 053055. In 2015 the bottom 50 per cent in China earn approximately 15 per cent of total national income versus 12 per cent in the USA and 22 per cent in France. As China experienced rapid economic growth in the mid-1980s it also faced an accompanying downside. Although it has been improving Chinas income inequality has actually been one of the worse in the world with 1 of the population owning 13rd of Chinas wealth reinforced by the fact that Chinas GINI coefficient was in the high forties from 2006-2013. Meanwhile President Xi Jinping has a net worth exceeding 15 billion. The official Gini coefficient an index that measures income distribution showed that after falling for eight straight years to 2015 inequality rose between 2016 and 2018.
Using multiple data sources we establish that Chinas income inequality since 2005 has reached very high levels with the Gini coefficient in the range of 053055.
Meanwhile President Xi Jinping has a net worth exceeding 15 billion. The Gini Index is a statistical. This trend has started to reverse as China has experienced a modest decline in inequality since 2008. This paper reviews the historical trends and patterns of income. It can clearly be seen that the share of the wealth going to the top 10 percent has been consistently going up since the year 1978 this is the year when the country liberalized its economy. However income inequality increased sharply from the early 1980s and rendered China among the most unequal countries in the world.