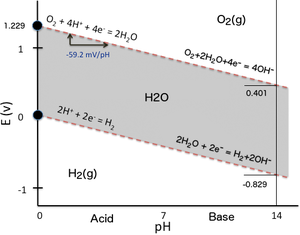
How To Read Pourbaix Diagram. The Pourbaix diagram is an ordinary potential phase diagram for H 2 O and selected contents of the additional components. 90 In more concentrated sulfuric acid solutions of. The diagram is sectioned at the temperature and pressure of interest usually 25C and 1. Diagrams represent the stability of a metal as a function of potential and pH.
However both recent advances in high-throughput material exploration and increasing complexity of materials of interest for electrochemical applications pose challenges for performing Pourbaix analysis on multidimensional systems. As noted above these diagrams are essentially phase diagrams that plot the map the. The Pourbaix diagram can be thought of as analogous to a phase. M M z ze-depend on various factors including the potential E pH and the concentration of the oxidised species M z. At a particular combination of pH and potential a stable phase can be determined from the Pourbaix diagram. The Pourbaix diagram is a projection of the equilibrium potential surface in a many dimensional parameter space onto the subspace of pH.
Pourbaixs diagram predicts that Pt metal will dissolve as Pt 2 during anodic polarization in strong acid solutions.
In an Eh-pH diagram the solid stability area is related to the saturation condition and dominant aqueous species give us fundamental information on sorption and colloid phenomena as well as surface characteristics of materials. The extent of half-cell reactions that describe the dissolution of metal. High E values represent an oxidizing environment. The Pourbaix diagram can be thought of as analogous to a phase. The pE scale is intended to represent the concentration of the standard reducing agent the e- analogously to the pH scale representing the concentration of standard acid H. Pourbaix Diagrams plot electrochemical stability for different redox states of an element as a function of pH.