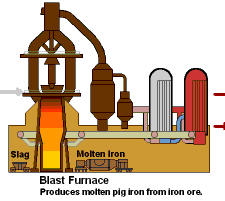
How A Blast Furnace Works. In the blast furnace production iron ore coke and slag-forming flux limestone are charged from the top of the furnace and preheated air is blown from the tuyere located at the lower portion of the furnace along the circumference of the furnace. 185m boost for Corus steel plant. Basically the blast furnace is a countercurrent heat and oxygen exchanger in which rising combustion gas loses most of its heat on the. The Blast Furnace is a large steel structure about 30 metres high.

The purpose of a blast furnace is to chemically reduce and physically convert iron oxides into liquid iron called hot metal. A blast furnace also represents a huge overhead cost because once fired up it typically runs for six to 10 years giving an operator little flexibility. The raw materials require 6 to 8 hours to descend to the bottom of the furnace where. The blast furnace is a huge steel stack lined with refractory brick where iron ore coke and limestone are dumped into the top and preheated air is blown into the bottom. Its two blast furnaces and steel production plant buildings are major landmarks visible from both the M4 motorway and the South Wales Main Line when passing through the town. Add Fuel to the Blast Furnace.
The Blast Furnace is a large steel structure about 30 metres high.
Nicola Smith explains what a blast furnace does and why its so important to the plants steelmaking capabilities. A simplified diagram of a Blast Furnace is drawn below. 2 The limestone breaks down to form more carbon dioxide and calcium oxide which would be used later on. Steps to Use a Blast Furnace 1. In this tutorial we are going. Blast furnaces produce pig iron from iron ore by the reducing action of carbon supplied as coke at a high temperature in the presence of a fluxing agent such as limestone.