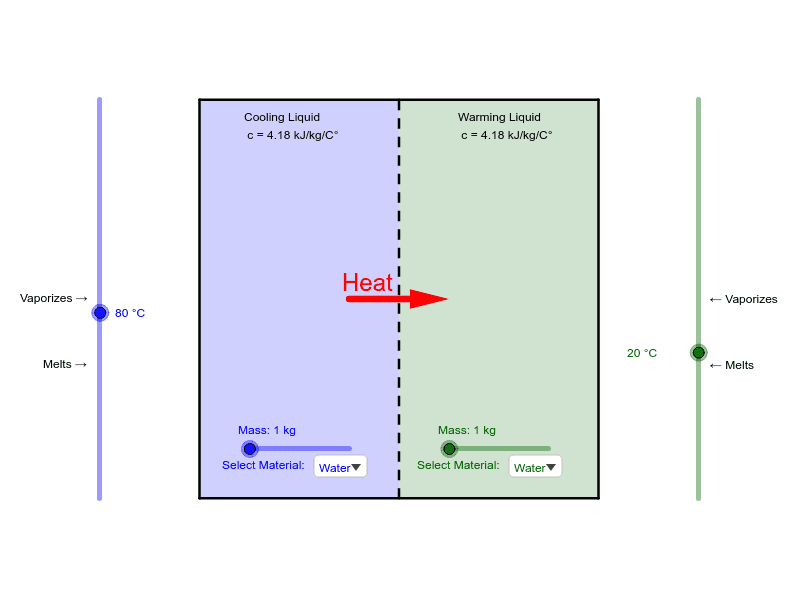
During A Phase Change Mass. Morrison Michigan Tech U. The energy per unit mass required to change a substance from the liquid phase to the vapor phase is known as the heat of vaporization. The mass of the substance does not change due to the conservation of mass. To determine these terms the interface between the gaseous and the liquid phases is described by a separating immaterial smooth surface together with.
Therefore the local heat transfer coefficient decreased along the flow direction due to the decreasing contribution of phase change to the heat exchange. Put a cup of water in the freezer and it will change to a solid. The energy involved in a phase change depends on two major factors. During a phase change. Substance the first phase transitions discovered other thermodynamic phase changes occur in Nature as the change from normal electrical conductivity to superconductivity with or without magnetic field the change from paramagnetism to ferromagnetism the change from normal viscosity to superfluidity in. During a phase change.
In the thermally fully-developed region mass transfer rate from the solid particles to liquid phase decreased because the rapid decrease of solid volume fraction near the wall impeded the phase change.
The strength of forces depends on the type of molecules. Put it out in the sun and eventually the liquid will disappear. To determine these terms the interface between the gaseous and the liquid phases is described by a separating immaterial smooth surface together with. The instantaneous heat transfer rate during the melting process must be known for optimal system design and operation of the application. Therefore the local heat transfer coefficient decreased along the flow direction due to the decreasing contribution of phase change to the heat exchange. The strength of forces depends on the type of molecules.