Definition Of Structural Fatigue. Fatigue is the progressive and localized structural damage that occurs when a material is subjected to cyclic loading. These are discussed in more detail in Fricke 2001 and illustrated in Fig3. This type of structural damage occurs even when the experienced stress range is far below the static material strength. The level of sophistication The level of sophistication required in the analysis in terms of structural modeling and boundary conditions ie soil-structure.

If the local stresses are high enough this leads to the initiation of a crack the growth of the crack and finally fracture. Material fatigue is a phenomenon where structures fail when subjected to a cyclic load. The stresses could be due to vibration or thermal cycling. The structural stress definition is consistent with elementary structural mechanics theory and provides an effective measure of a stress state that pertains to fatigue behavior of welded joints in. Fatigue failure is defined as the tendency of a material to fracture by means of progressive brittle cracking under repeated alternating or cyclic stresses of an intensity considerably below the normal strength. Stresses in the structure both fatigue and operational maximum stresses that cause crack growth from the damaged condition geometry of the material which intensifies or reduces the stresses on the crack tip ability of the material to withstand cracking due to stresses in the expected environment.
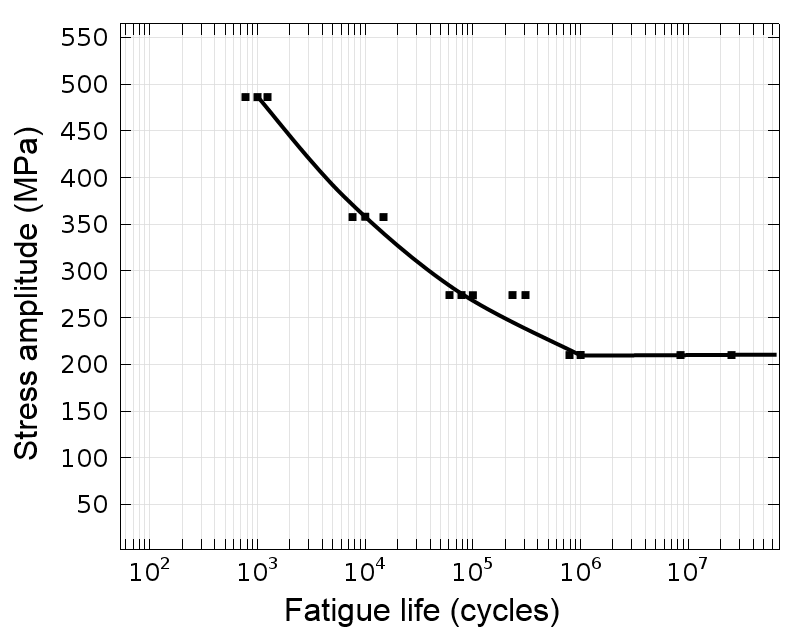
Fatigue test results obtained from transverse butt welds expressed in terms of the measured stress range.
Structural Mechanics Material Fatigue What Is Material Fatigue. In reviewing the hot-spot stress S-N data attention was focused on just three of the various definitions of the hot-spot stress. 1- What is Fatigue Failure. Browse the use examples fatigue reliability of structure in the great English corpus. Fatigue demand is to be determined usingan appropriate structural analysis. Structural Fatigue is the process where a compound begins to develop cracks when loaded with a time-varying load.