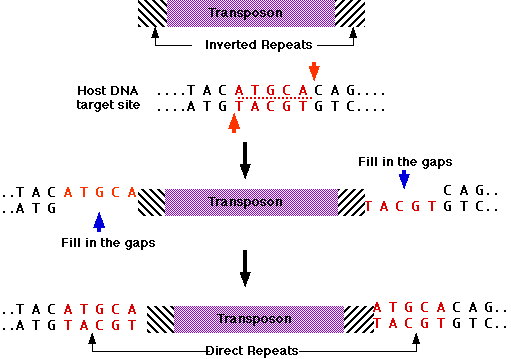
Compare The Way Transposons And Exons Affect Genes. In order for the transposon to alter phenotype it has to jump into an exon or the control region of the gene. Usually the Class II type is referred as the transposons and the Class I type is referred as the retrotransposons. However most of the TEs are inactive in the humans and other higher eukaryotes. The transposons are the major game changer in the field of plant genetics.

Right-angled arrows represent gene. Most organisms have inactive transposons. Another way in which transposons facilitate germ line cell exon shuffling is more direct. Transposons are of two major types known as Class I Transposons and Class II Transposons. Inserting into a non-coding region like an intron will have no effect unless the insertion disrupts the exonintron splice junctions. DNA transposons encode transposases that must recognize and bind to the transposon itself to rep- licate it.
Most organisms have inactive transposons.
Some transposition events inactivate genes since the coding potential or expression of a gene is disrupted by insertion of the transposable element. The enzyme binds to the both ends of the transposon and cuts the. A brief outline of the process of the central dogma. Blue boxes represent TEs gray boxes represent canonical exons and the black box represents a sequencing read. Compare the way transposons and exons affect genes. Transposon class of genetic elements that can jump to different locations within a genome.