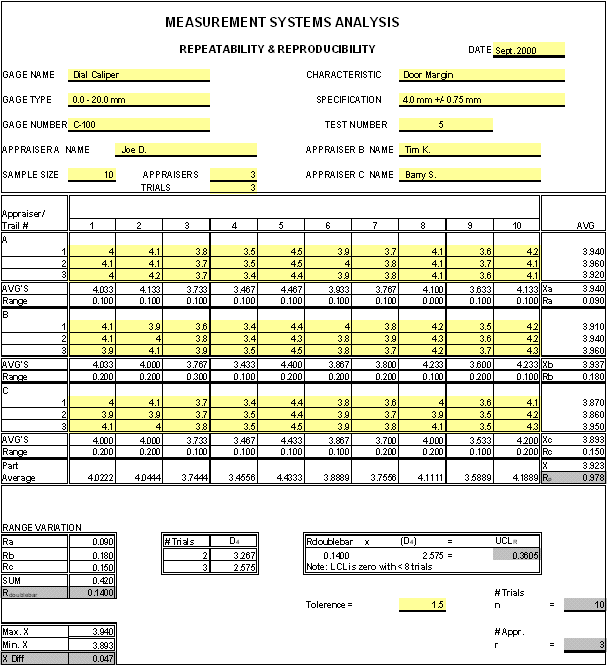
Bias Study Measurement System Analysis. A point estimate is a single value that is the best estimate of the true unknown parameter. The bias meaning the average difference between the measured value and the reference value is significantly large The software decides this based on the 95 confidence bounds which are a type of t. Bias is a measure of a systematic measurement error the component of measurement error that remains constant in replicate measurements. BIAS AVERAGE MEASUREMENT REFERENCE VALUE.
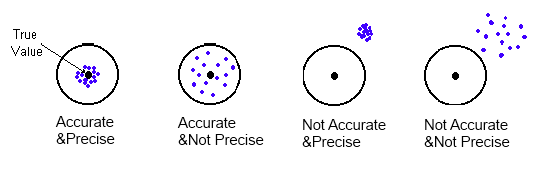
The study assesses linearity how accurate your measurements are through the expected range of measurements and bias how well your measurements compare to a reference value. The point of the gage linearity and bias study is to detect whether your measurements are harder to take as they get bigger or smaller. BIAS AVERAGE MEASUREMENT REFERENCE VALUE. Figure 2 shows the bias analysis as presented in the stability module of GAGEtrak software. Well get to study consistency more formally soon with a Gage RR study. If the true value is unknown it can be calculated by averaging several measurements with the most accurate measuring equipment available.
Well get to study consistency more formally soon with a Gage RR study.
The reference value is an agreed value depending on the specification of the process product. Select a cell in the dataset. The bias meaning the average difference between the measured value and the reference value is significantly large The software decides this based on the 95 confidence bounds which are a type of t. A point estimate is a single value that is the best estimate of the true unknown parameter. What is Measurement System Analysis MSA MSA is defined as an experimental and mathematical method of determining the amount of variation that exists within a measurement process. Estimating the bias of a measurement system Estimate the trueness of a measurement system or measurement procedure.